

11.3 Estimation: Fixed-effects (FE) estimator.
 11.2 Estimation: First-difference (FD) estimator. 8.10.6 Matching on more variables and polynomials. 8.10.5 Genetic Matching: Single variable. 8.5 Exercise: Logic of & varieties of matching. 7.6 Pervasive problem: Example post-treatment bias. 7.5 Covariates: Endogenous selection bias. 7.4 Covariates: Confounding/overcontrol bias. 6.8 Natural experiments: Challenges & Criticism. 6.3 Ideal experiments: Possible “ideal” design. 5.4.1 Long-run randomization & balance (not finished). 5.4 Lab: How randomization induces independence. 4.34 Identification Analysis & Strategy. 4.33 Causes: Manipulable causes (Discussion). 4.32 Causes: No causation without manipulation. 4.31 Causes: Which variables are causes? (Discussion). 4.29 Exercise: Treatments/outcome as trajectories. 4.27 ATT: Average Effect of the Treatment on the Treated and the Control. 4.23 Independence assumption & random assignment. 4.22 Assumptions: Independence Assumption (IA). 4.21 Assumptions: Independence Assumption (IA). 4.16 Why moving from ITE to ATE? (Wikipedia). 4.10 Definition of Treatment/Causal Effect. 4.9 Potential outcomes (multiple treatment values) (skip!). 4.5 Causal chains & causal mechanism (3). 4.4 Causal chains & causal mechanism (2). 4.3 Causal chains & causal mechanism (1).
11.2 Estimation: First-difference (FD) estimator. 8.10.6 Matching on more variables and polynomials. 8.10.5 Genetic Matching: Single variable. 8.5 Exercise: Logic of & varieties of matching. 7.6 Pervasive problem: Example post-treatment bias. 7.5 Covariates: Endogenous selection bias. 7.4 Covariates: Confounding/overcontrol bias. 6.8 Natural experiments: Challenges & Criticism. 6.3 Ideal experiments: Possible “ideal” design. 5.4.1 Long-run randomization & balance (not finished). 5.4 Lab: How randomization induces independence. 4.34 Identification Analysis & Strategy. 4.33 Causes: Manipulable causes (Discussion). 4.32 Causes: No causation without manipulation. 4.31 Causes: Which variables are causes? (Discussion). 4.29 Exercise: Treatments/outcome as trajectories. 4.27 ATT: Average Effect of the Treatment on the Treated and the Control. 4.23 Independence assumption & random assignment. 4.22 Assumptions: Independence Assumption (IA). 4.21 Assumptions: Independence Assumption (IA). 4.16 Why moving from ITE to ATE? (Wikipedia). 4.10 Definition of Treatment/Causal Effect. 4.9 Potential outcomes (multiple treatment values) (skip!). 4.5 Causal chains & causal mechanism (3). 4.4 Causal chains & causal mechanism (2). 4.3 Causal chains & causal mechanism (1).  4.2 Deterministic vs. probabilistic causation. 4 Causal Analysis: Concepts & Definitions. 3.22 Models: Associational vs. causal inference. 3.21 Models: Estimand, estimator and estimation (skip). 3.18 Models: Example: Linear model (Visualization). 3.17 Models: Example: Linear model (Equation). 3.13 Data: Probability Distributions & Inference. 3.10 Data: (Empirical) Joint distributions. 3.9 Data: (Empirical) Univariate distributions. 3.5 Measurement: Scenarios, planned and realized measurements.
4.2 Deterministic vs. probabilistic causation. 4 Causal Analysis: Concepts & Definitions. 3.22 Models: Associational vs. causal inference. 3.21 Models: Estimand, estimator and estimation (skip). 3.18 Models: Example: Linear model (Visualization). 3.17 Models: Example: Linear model (Equation). 3.13 Data: Probability Distributions & Inference. 3.10 Data: (Empirical) Joint distributions. 3.9 Data: (Empirical) Univariate distributions. 3.5 Measurement: Scenarios, planned and realized measurements. 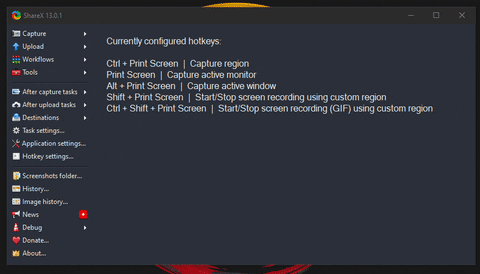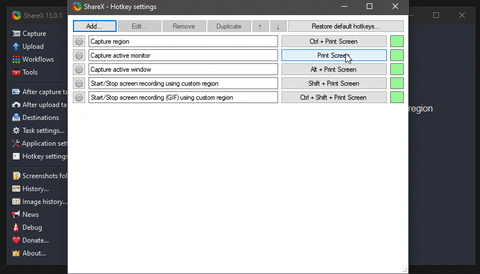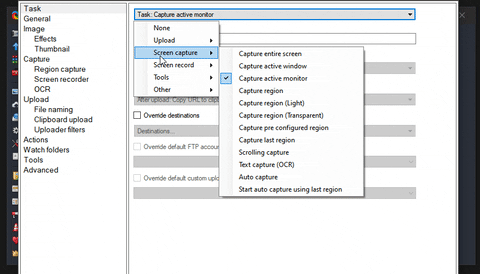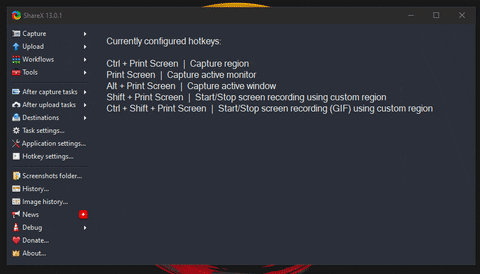
3.4 Measurement: Distribution(s) of measurements.3 Introduction: Fundamental statistical concepts.1.4 Motivation: The causal inference ‘revolution’.1 Introduction: About this seminar/book.












